Partial Key Verification Library for Compact Framework
This is fork of cuda/Partial-Key-Verification ported for .NET Compact Framework 3.5. Compile using Visual Studio 2008 Professional with installed SDK for Windows Mobile 6.
Partial Key Verification
Partial Key Verification (PKV) is a software licensing key technique that breaks a product key into multiple subkeys. With each version of your software, you check a different subset of the subkeys. The beauty of this approach is that a cracker cannot generate a complete keygen. They might be able to generate one for a given version, but it won't work on a different release (assuming you check a different subkey). Another nice feature of PVK is that the key contains an embedded serial number. This allows you to easily check the key against a list of stolen/posted/refunded keys. For more information about the PKV technique, see this blog post by Brandon Staggs.
This version of PKV differs slightly from the one discussed by Brandon Staggs.
Instead of using 8-bit subkeys, I used 32-bit subkeys (just check one key instead
of four). My version also Base-32 (5-bit) encodes the keys to shrink the key size
by 20%, and allows you to specify a different hash algorithm for each subkey.
Setup
At this moment, there is no build artifacts available to download from GitHub Releases. You need to clone the repository and build it yourself using Visual Studio 2008 Professional with Compact Framework 3.5 installed.
GitHub RepositoryAfter successful build, there will be few artifacts:
PartialKeyVerificationLibrary.Generator- Library for generating serial keys. Using this library, you can create your own KeyGen application or web service instead of using provided oneKeyGenerator.Desktop.PartialKeyVerificationLibrary.Verificator- Library used for validating correctness of provided serial keys.KeyGenerator.Desktop- Tool for easy secret's randomization, serial generation and validator code generation. See Quick Start.KeyGenerator.Desktop.Setup- Installer forKeyGenerator.Desktopapplication.DemoApplication.Mobile- Screenshot bellow. Sample Windows Mobile app to present generation and validation of serial keys.
Application: DemoApplication.Mobile
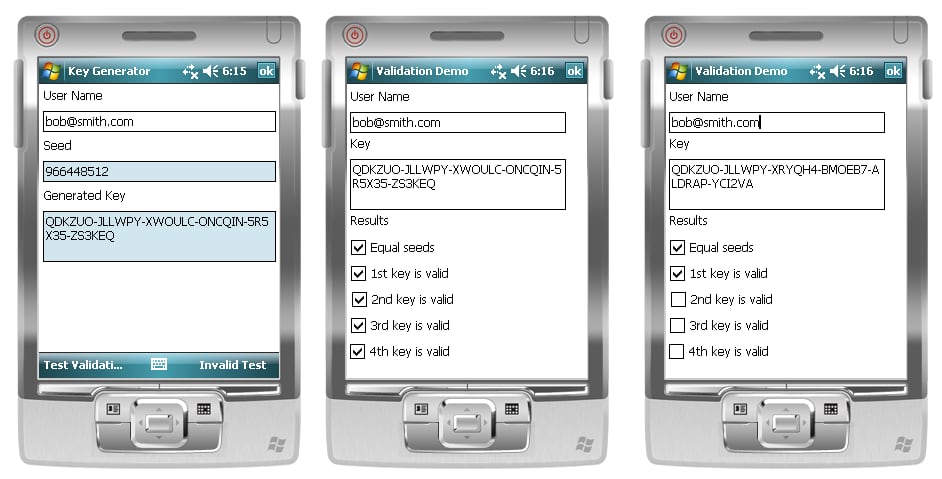
Usage
Quick Start
- Start
KeyGenerator.Desktoptool.
- Select New Definition from File menu.
- Choice number of generated keys and press Create. When prompted, save your generated keys on disk.
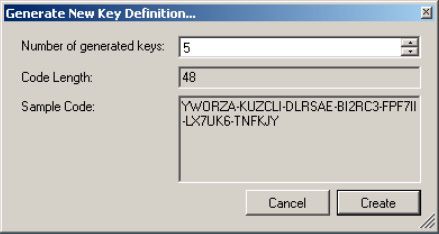
- Now, in main window, you can provide username to generate serial numbers.
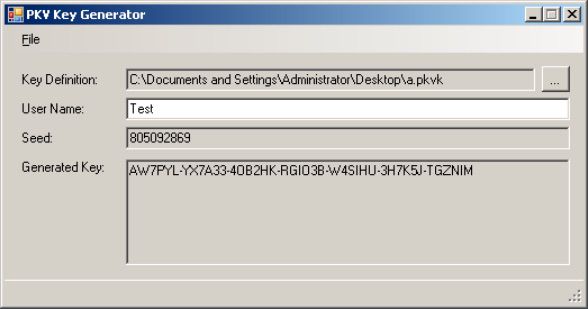
- Select Generate Code from File menu.
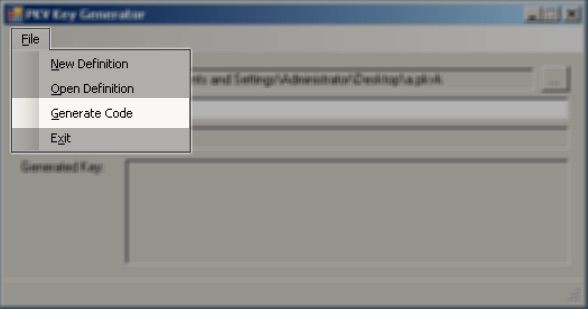
- Enable options as needed, and choice few keys to verify.
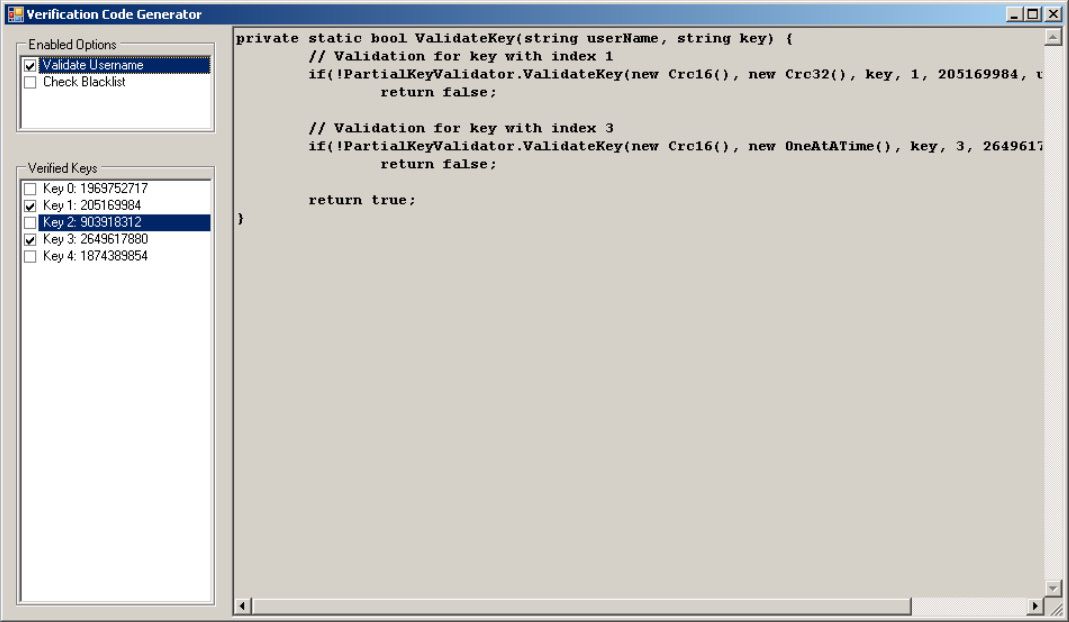
- Generated function can be used in your project to validate serial keys.
PartialKeyVerificationLibrary.Generator API
To generate a key, create a PartialKeyGenerator class specifying the checksum and hash functions to use, along with the base values for each subkey. Then call the Generate function, passing it a serial number or a string (such as the customer's e-mail address) to generate a key. You can optionally tell the generator to add a separator between a certain number of characters in the key by setting the Spacing property.
var generator = new PartialKeyGenerator(new Adler16(), new Jenkins96(), new uint[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }) { Spacing = 6 };var key = generator.Generate("bob@smith.com");This will generate the key: QDKZUO-JLLWPY-XWOULC-ONCQIN-5R5X35-ZS3KEQ. Adler16 is the checksum function and Jenkins96 is the hash function. You can have as many subkeys as you like, but each subkey adds 7 more characters to the key.
PartialKeyGenerator
Constructors:
PartialKeyGenerator(KeyDefinition definition)KeyDefinition definition- Serial generation definition
PartialKeyGenerator(IChecksum16 checksum, IHash hash, uint[] baseKeys)IChecksum16 checksum- The checksum algorithm to use.IHash hash- The hash algorithm to use.uint[] baseKeys- The integer bases keys used to generate the sub keys (one base key for each sub key).
PartialKeyGenerator(IChecksum16 checksum, IEnumerable<IHash> hashFunctions, uint[] baseKeys)IChecksum16 checksum- The checksum algorithm to use.IEnumerable<IHash> hashFunctions- A list of hash functions to use. If the number of hash functions is less than the number `baseKeys, then the functions cycles back to the first function. It is recommended to use several different hash functions.uint[] baseKeys- The integers used to generate the sub key.
Properties:
byte Spacing- The spacing of the key separator.
Methods:
string Generate(uint seed)- Generate a key based on the given seed.
uint seed- The seed value to generate the key from.- Returns a licensing key.
string Generate(string seed)- Generate a key based on the given string seed. Generate will hash the given string to create an uint seed.
string seed- The seed value to generate the key from.- Returns a licensing key.
IDictionary<uint, string> Generate(uint numberOfKeys, Random random)- Generates a set of random keys.
uint numberOfKeys- The number of keys to generate.Random random- The random number generator to use.- Returns a set of randomly generate keys.
Key Definitions
For ease of use, there is prepared format for storing and retrieving key definition in a file.
When saved with .pkvk file extension, definitions are interchangeable with KeyGenerator.Desktop tool.
There is also generation tool for generating definitions and verification code for automated pipelines.
int numberOfKeys = 10;KeyDefinition definition = DefinitionGenerator.MakeDefinition(numberOfKeys);PartialKeyVerificationLibrary.Verificator API
To validate the key, use the PartialKeyValidator static class. Again telling it the checksum and hash functions to use, along with which subkey to check and the base value for that subkey. For example, to check the first subkey of the key generated above:
var isValid = PartialKeyValidator.ValidateKey(new Adler16(), new Jenkins96(), key, 0, 1);PartialKeyValidator
Static methods:
bool ValidateKey(IChecksum16 checksum, IHash hash, string key, int subkeyIndex, uint subkeyBase)- Validates the given key. Verifies the checksum and each sub key.
IChecksum16 checksum- The hash algorithm used to compute the sub key.IHash hash- The checksum algorithm used to compute the key's checksum.string key- The key to validate.int subkeyIndex- The index (zero based) of the sub key to check.uint subkeyBase- The unsigned base integer used create the sub key.- Returns
trueif thekeyis valid;falseotherwise.
bool ValidateKey(IChecksum16 checksum, IHash hash, string key, int subkeyIndex, uint subkeyBase, string seedString)- Validates the given key. Verifies the given string seed matches the seed embedded in the key, verifies the checksum and each sub key. This version is useful if the seed used to generate a key was derived from some user information such as the user's name, e-mail, etc.
IChecksum16 checksum- The hash algorithm used to compute the sub key.IHash hash- The checksum algorithm used to compute the key's checksum.string key- The key to validate.int subkeyIndex- The index (zero based) of the sub key to check.uint subkeyBase- The unsigned base integer used create the sub key.string seedString- The string used to generate the seed for the key.- Returns
trueif thekeyis valid;falseotherwise.
uint GetSerialNumberFromKey(string key)- Extracts the serial number from a key.
string key- The key to extract the serial number from.- Returns the serial number embedded in the key.
uint GetSerialNumberFromSeed(string seed)- Converts a string seed into a serial number (uint seed).
string seed- The string seed to convert.- Returns the string seed converted to a serial number.
Sample validation code
bool ValidateKey(string userName, string key){ var seed = PartialKeyValidator.GetSerialNumberFromKey(key); var blacklist = new List<uint> { 1518008798, }; if (blacklist.Contains(seed)) return false; // Validation for key with index 1 if (!PartialKeyValidator.ValidateKey(new Adler16(), new OneAtATime(), key, 1, 766109221, userName)) return false; // Validation for key with index 4 if (!PartialKeyValidator.ValidateKey(new Adler16(), new SuperFast(), key, 4, 4072442218, userName)) return false; return true;}Available Checksum Algorithms
Checksum.Adler16Checksum.Crc16Checksum.CrcCcitt
Available Hashing Algorithms
Hash.Crc32Hash.Fnv1AHash.GeneralizedCrcHash.Jenkins06Hash.Jenkins96Hash.OneAtATimeHash.SuperFast